Installation
Note
The library has been tested against Python 3.6 and newer.
Pre-requisites
MAX7219 Devices
By default, the SPI kernel driver is NOT enabled on a Raspberry Pi Raspbian image. You can confirm whether it is enabled using the shell command below:
$ lsmod | grep -i spi
spi_bcm2835 7424 0
Depending on the hardware/kernel version, this may report spi_bcm2807 rather than spi_bcm2835 - either should be adequate.
And to verify that the devices are successfully installed in /dev:
$ ls -l /dev/spi*
crw------- 1 root root 153, 0 Jan 1 1970 /dev/spidev0.0
crw------- 1 root root 153, 1 Jan 1 1970 /dev/spidev0.1
If you have no /dev/spi files and nothing is showing using lsmod then this
implies the kernel SPI driver is not loaded. Enable the SPI as follows (steps
taken from https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/raspberry-pi-spi-and-i2c-tutorial#spi-on-pi):
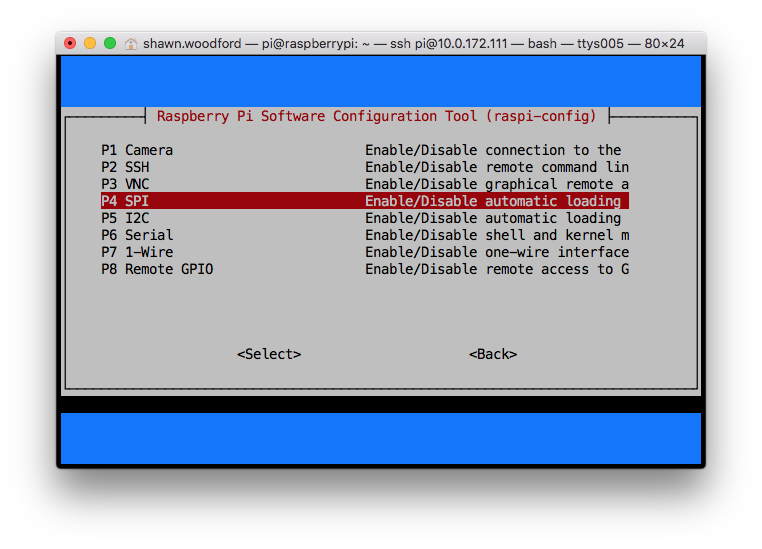
Run
sudo raspi-configUse the down arrow to select
5 Interfacing OptionsArrow down to
P4 SPISelect yes when it asks you to enable SPI
Also select yes when it asks about automatically loading the kernel module
Use the right arrow to select the <Finish> button
Reboot.
After rebooting re-check that the lsmod | grep -i spi command shows whether
SPI driver is loaded before proceeding. If you are stil experiencing problems, refer to the official
Raspberry Pi SPI troubleshooting guide
for further details, or ask a new question - but
please remember to add as much detail as possible.
GPIO pin-outs
MAX7219 Devices (SPI)
The breakout board has two headers to allow daisy-chaining:
Board Pin |
Name |
Remarks |
RPi Pin |
RPi Function |
1 |
VCC |
+5V Power |
2 |
5V0 |
2 |
GND |
Ground |
6 |
GND |
3 |
DIN |
Data In |
19 |
GPIO 10 (MOSI) |
4 |
CS |
Chip Select |
24 |
GPIO 8 (SPI CE0) |
5 |
CLK |
Clock |
23 |
GPIO 11 (SPI CLK) |
See also
Also see the section for cascading/daisy-chaining, power supply and level-shifting.
WS2812 NeoPixels (DMA)
Typically, WS2812 NeoPixels reqire VCC, VSS (GND) and DI pins connecting to the Raspberry Pi, where the DI pin is usually connected to a PWM control pin such as GPIO 18.
Board Pin |
Name |
Remarks |
RPi Pin |
RPi Function |
1 |
DO |
Data Out |
||
2 |
DI |
Data In |
12 |
GPIO 18 (PWM0) |
3 |
VCC |
+5V Power |
2 |
5V0 |
4 |
NC |
Not connected |
||
5 |
VDD |
Not connected |
||
6 |
VSS |
Ground |
6 |
GND |
The DO pin should be connected to the DI pin on the next (daisy-chained) neopixel, while the VCC and VSS are supplied in-parallel to all LED’s. WS2812b devices now are becoming more prevalent, and only have 4 pins.
NeoSegments
@msurguy’s NeoSegments should be connected as follows:
Board Pin |
Name |
Remarks |
RPi Pin |
RPi Function |
1 |
GND |
Ground |
6 |
GND |
2 |
DI |
Data In |
12 |
GPIO 18 (PWM0) |
3 |
VCC |
+5V Power |
2 |
5V0 |
Installing from PyPi
Install the dependencies for library first with:
$ sudo usermod -a -G spi,gpio pi
$ sudo apt install build-essential python3-dev python3-pip libfreetype6-dev libjpeg-dev libopenjp2-7 libtiff5
Warning
The default pip and setuptools bundled with apt on Raspbian are really old,
and can cause components to not be installed properly. Make sure they are up to date by upgrading
them first:
$ sudo -H pip install --upgrade --ignore-installed pip setuptools
Proceed to install latest version of the luma.led_matrix library directly from PyPI:
$ sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade luma.led_matrix
Examples
Ensure you have followed the installation instructions above. Clone the repo from github, and run the example code as follows:
$ python examples/matrix_demo.py
The matrix demo accepts optional flags to configure the number of cascaded devices and correct the block orientation phase shift when using 4x8x8 matrices:
$ python examples/matrix_demo.py -h
usage: matrix_demo.py [-h] [--cascaded CASCADED]
[--block-orientation {0,90,-90}] [--rotate {0,1,2,3}]
[--reverse-order REVERSE_ORDER]
matrix_demo arguments
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--cascaded CASCADED, -n CASCADED
Number of cascaded MAX7219 LED matrices (default: 1)
--block-orientation {0,90,-90}
Corrects block orientation when wired vertically
(default: 0)
--rotate {0,1,2,3} Rotate display 0=0_, 1=90_, 2=180_, 3=270_
(default: 0)
--reverse-order REVERSE_ORDER
Set to true if blocks are in reverse order (default:
False)
Similarly, there is a basic demo of the capabilities of the
luma.led_matrix.virtual.sevensegment wrapper:
$ python examples/sevensegment_demo.py
and for the luma.led_matrix.device.neopixel device:
$ sudo python examples/neopixel_demo.py
Further examples are available in the luma.examples. git repository. Follow the instructions in the README for more details.
A small example application using ZeroSeg to display TOTP secrets can be found in https://github.com/rm-hull/zaup.